Hypertension in Pregnancy: What You Need to Know
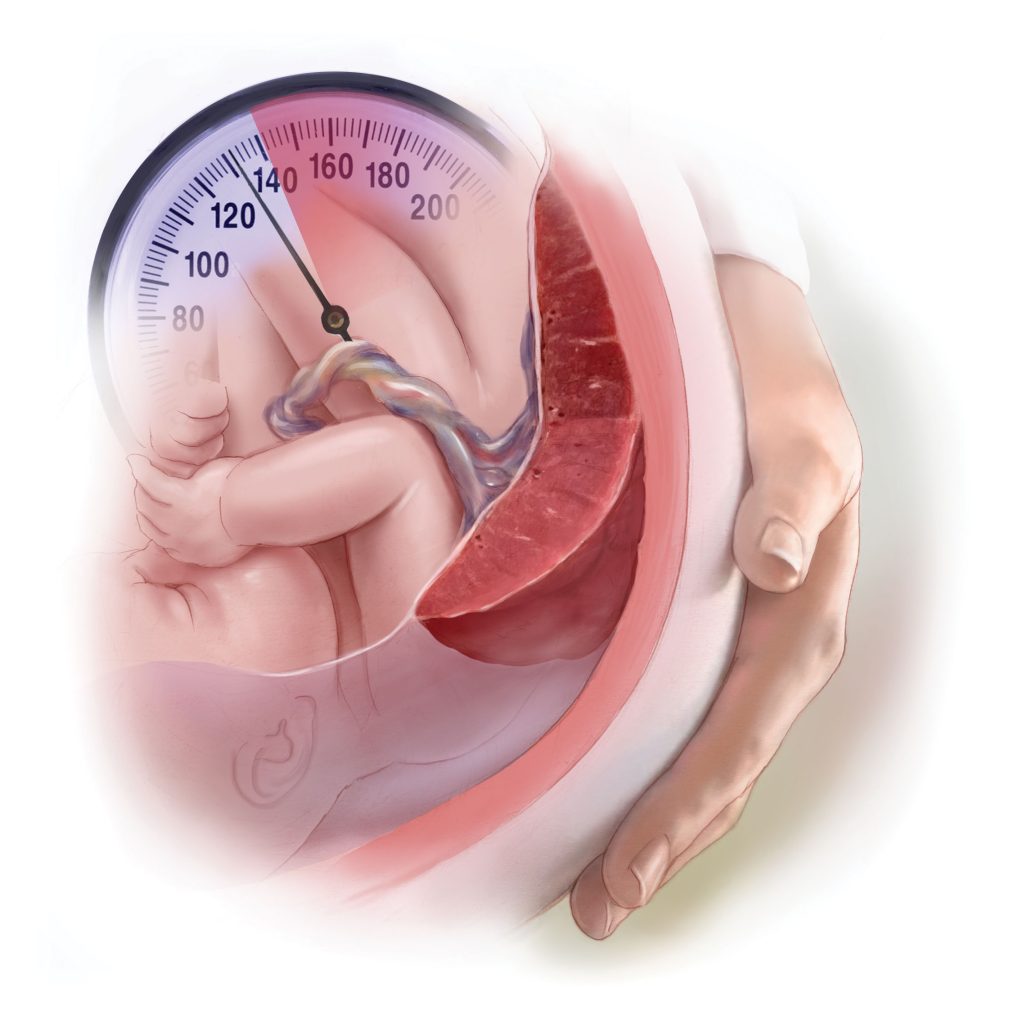
Hypertension during pregnancy, also known as gestational hypertension or pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH), is a condition that can pose significant risks to both the mother and the baby. Understanding the implications, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for ensuring a successful pregnancy with high blood pressure. The Relationship Between Diabetes and Hypertension During Pregnancy Diabetes and hypertension often coexist and can complicate pregnancy. Women with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing hypertension during pregnancy, which can lead to a range of complications including preeclampsia, preterm birth, and complications during delivery. Managing both conditions effectively is vital for maternal and fetal health. Normal Blood Pressure for Pregnant Women For most pregnant women, a normal blood pressure reading is below 120/80 mm Hg. However, blood pressure can vary throughout pregnancy, and slight elevations may not be immediately concerning. Regular monitoring is essential to catch any significant changes early. Low Blood Pressure During Pregnancy While high blood pressure garners most of the attention, low blood pressure during pregnancy can also be an issue. Symptoms like dizziness, fainting, and fatigue can be common. It is important to stay hydrated and avoid prolonged standing to manage these symptoms. When Should Swelling During Pregnancy Be a Concern? Swelling, particularly in the feet and ankles, is common during pregnancy. However, sudden or severe swelling, especially in the hands and face, can be a sign of preeclampsia, a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Why Do Doctors Prescribe Aspirin During Pregnancy? Doctors may prescribe low-dose aspirin during pregnancy to women who are at high risk of preeclampsia. Aspirin can help reduce the risk of developing this condition by improving placental blood flow and reducing inflammation. High Blood Pressure After Pregnancy High blood pressure can persist even after the baby is born, a condition known as postpartum hypertension. It is crucial to continue monitoring blood pressure levels and follow the doctor’s advice to manage this condition effectively. 120 Resting Heart Rate While Pregnant A resting heart rate of 120 beats per minute (bpm) can be higher than normal during pregnancy, where the typical range is 60-100 bpm. Increased heart rate can be due to the additional stress on the body as it supports the growing baby. If you notice consistently high heart rates, consult your healthcare provider. When Do You Start Showing Second Pregnancy? In the second pregnancy, women often start showing earlier than they did in their first pregnancy. This is due to the abdominal muscles being stretched from the previous pregnancy. Typically, women begin to show between 12 to 16 weeks. Managing PIH Pregnancy for a Successful Outcome Successfully managing PIH involves regular prenatal check-ups, lifestyle modifications, and possibly medication. Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking and alcohol can help manage blood pressure levels. Key Takeaways for Managing Hypertension During Pregnancy By understanding the risks and taking proactive steps, pregnant women with hypertension can improve their chances of a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Navigating Brilinta and Eliquis: A Comprehensive Comparison

Brilinta and Eliquis are both widely prescribed medications used to treat different cardiovascular conditions. While they serve similar purposes, there are important differences between them that patients and healthcare providers should be aware of. In this article, we’ll delve into the similarities, differences, and considerations when using Brilinta and Eliquis, including potential interactions and side effects. Brilinta vs Eliquis: Understanding the Differences Brilinta and Eliquis Together One common question among patients is whether Brilinta and Eliquis can be taken together. While there is no direct contraindication to using these medications simultaneously, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure appropriate dosing and monitoring. Does Brilinta Cause Weight Gain? Weight gain is not a commonly reported side effect of Brilinta. However, individual responses to medications can vary, and some patients may experience weight changes while taking Brilinta. It’s essential to discuss any concerns or changes in weight with a healthcare provider. What to Avoid When Taking Brilinta? When taking Brilinta, it’s important to avoid certain medications and substances that may interact with it. These include other blood-thinning medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and certain herbal supplements like ginkgo biloba and garlic. Xarelto 20 mg Equivalent Eliquis Xarelto and Eliquis are both anticoagulant medications used to prevent blood clots. While there is no direct equivalent dose between Xarelto 20 mg and Eliquis, healthcare providers can determine the appropriate dosage based on individual patient factors and medical history. Key Takeaways Conclusion Understanding the similarities, differences, and considerations when using Brilinta and Eliquis is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. By working closely with a healthcare provider and staying informed about potential interactions and side effects, patients can optimize their treatment and improve their cardiovascular health outcomes.
Exploring Alternatives to Creon: Finding Digestive Relief Naturally
When it comes to managing digestive issues like pancreatic insufficiency, Creon is a commonly prescribed medication. However, some individuals may seek alternatives for various reasons, such as cost, accessibility, or preference for natural remedies. In this article, we’ll delve into alternative options to Creon, including natural substitutes and over-the-counter alternatives, to help you find digestive relief. Creon Alternatives: Understanding Your Options Creon Alternatives Over the Counter For individuals seeking over-the-counter alternatives to Creon, several options are available. These include digestive enzyme supplements containing similar enzymes to those found in Creon, such as amylase, lipase, and protease. Brands like Pancreaze, Viokace, and Pertzye are commonly used alternatives to Creon that can aid in digestion. Natural Alternatives to Creon Some individuals prefer natural remedies for managing digestive issues. Digestive enzyme supplements derived from natural sources, such as papaya or pineapple, may provide relief for mild digestive discomfort. Additionally, incorporating foods rich in digestive enzymes, such as kiwi, ginger, and fermented foods, like sauerkraut and kimchi, into your diet may support digestion naturally. Vegetarian Alternatives to Creon For individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet, vegetarian-friendly alternatives to Creon are available. These alternatives typically contain plant-based enzymes sourced from fruits, vegetables, or fungi, providing digestive support without animal-derived ingredients. Pancreaze vs. Creon: Comparing Digestive Enzyme Supplements Pancreaze and Creon are both prescription medications used to treat pancreatic insufficiency. While they contain similar enzymes, such as lipase, amylase, and protease, their formulations and dosages may vary. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine which option is best suited to your individual needs and preferences. Finding Your Digestive Warrior: Exploring Your Options Ultimately, finding the right digestive solution is a personal journey. Whether you choose Creon, an over-the-counter alternative, or a natural remedy, it’s essential to listen to your body and work closely with your healthcare provider to find the best approach for managing your digestive health. Conclusion While Creon is a widely prescribed medication for pancreatic insufficiency, alternatives exist for those seeking different options. Whether you opt for over-the-counter alternatives, natural remedies, or vegetarian-friendly options, there are numerous choices available to support your digestive health journey. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment plan, and listen to your body’s needs as you explore alternative options for digestive relief.
Cantaloupe – Implications for Diabetes Management

Can a Diabetic Eat Cantaloupe? Exploring the Impact on Blood Sugar Levels One common query among individuals with diabetes is, “Can a diabetic eat cantaloupe?” The answer lies in understanding how cantaloupe affects blood sugar levels and its overall nutritional value for diabetes management. Cantaloupe is a delicious and refreshing fruit that is low in calories and rich in essential nutrients like vitamins A and C. However, its impact on blood sugar levels can vary, making it a topic of interest for individuals with diabetes. Is Cantaloupe Good for Diabetes? Understanding its Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Are cantaloupes good for diabetics? Understanding the glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) of cantaloupe can provide valuable insights into its suitability for individuals with diabetes. Can Diabetics Eat Cantaloupe and Honeydew Melon? Exploring the Benefits and Risks For individuals managing diabetes, making informed choices about fruits like cantaloupe and honeydew melon is essential. Let’s delve into whether diabetics can eat cantaloupe and honeydew melon without compromising their blood sugar control. Cantaloupe and Blood Sugar: Examining the Impact on Diabetes Type 2 Understanding how cantaloupe affects blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes type 2. Let’s explore whether cantaloupe is a suitable fruit choice for managing blood sugar levels in diabetes type 2. Cantaloupe for Diabetics: Assessing its Glycemic Load and Nutritional Benefits Can diabetics benefit from including cantaloupe in their diet? Examining the glycemic load of cantaloupe and its nutritional profile can provide valuable insights into its role in diabetes management. Honeydew for Diabetics: Evaluating its Impact on Blood Sugar Control Is honeydew melon a suitable fruit choice for individuals with diabetes? Let’s assess whether honeydew melon is good for diabetics and its potential impact on blood sugar control. Will Cantaloupe Raise Blood Sugar? Understanding its Glycemic Index and Effect on Blood Glucose Levels Concerned about whether cantaloupe will raise blood sugar levels? Let’s explore the glycemic index of cantaloupe and its potential impact on blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes. These articles aim to provide comprehensive information on the relationship between cantaloupe, honeydew melon, and diabetes, helping individuals make informed dietary choices for optimal diabetes management.
Protecting Your Baby from Gestational Diabetes
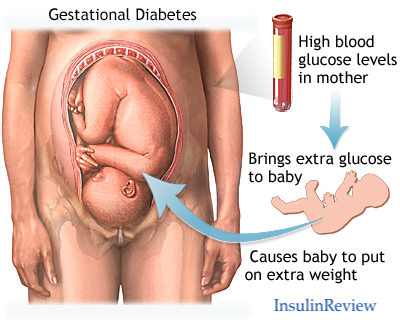
Are you expecting a new addition to your family? Congratulations! Pregnancy is an exciting time, but it’s essential to be aware of health concerns like gestational diabetes, which can have surprising long-term effects on your child’s health. What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that happens during pregnancy when the body can’t make enough insulin to handle the extra demand, causing high blood sugar levels. It usually shows up around the 24th week of pregnancy and can affect both the mother and the baby. Common Signs of Gestational Diabetes Look out for signs like needing to pee more often, feeling extra thirsty, tiredness, unusual weight changes, blurry vision, nausea, increased hunger, slow wound healing, or more frequent infections. If you notice any of these, talk to your doctor. Causes and Risk Factors Gestational diabetes can be caused by hormonal changes during pregnancy, genetics, being overweight, age, previous gestational diabetes, or conditions like PCOS. How Gestational Diabetes Affects Babies Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes might be larger than average, have low blood sugar after birth, face breathing problems, or have jaundice. They’re also more likely to become obese or develop type 2 diabetes later on. Protecting Your Baby’s Future You can lower the risks by: Conclusion: Safeguarding Your Baby’s Health Gestational diabetes may seem like a temporary concern during pregnancy, but its long-term effects on your child’s health can be significant. By understanding the risks, recognizing the signs, and taking proactive steps, you can protect your baby’s future. Here are some key recommendations: Remember, your proactive efforts during pregnancy can have a lasting impact on your child’s health and well-being. By prioritizing self-care, staying informed, and maintaining open communication with your healthcare team, you can navigate gestational diabetes with confidence and ensure a healthy start for your little one.
Understanding High Blood Pressure Guide
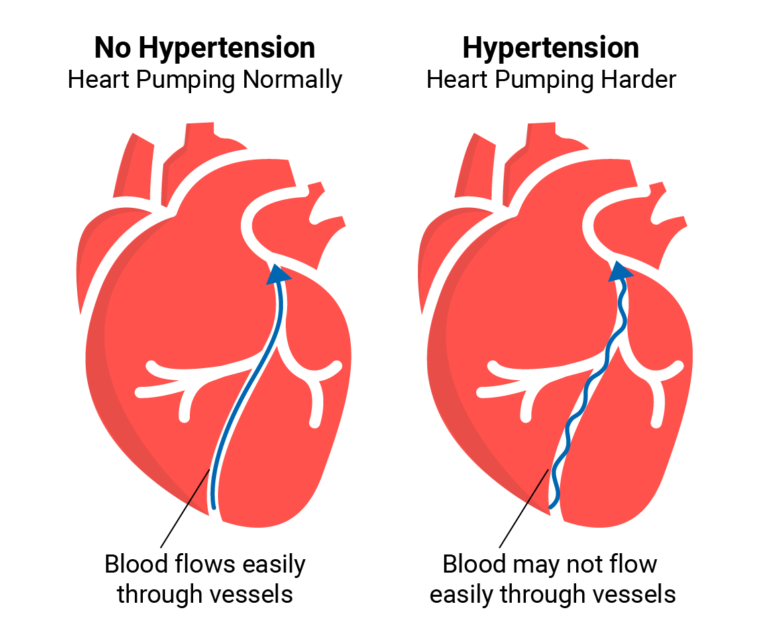
In this comprehensive blog post, we delve into the complexities of high blood pressure, providing readers with valuable insights and information to better understand this common yet often overlooked condition. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or seeking to learn more about hypertension, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to manage your health effectively. The Four Stages of Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is typically categorized into four stages based on blood pressure readings. Understanding these stages can help individuals and healthcare providers assess the severity of the condition and determine appropriate treatment strategies. Blood Facts: What You Need to Know Blood plays a vital role in the body, transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from cells. Learning about blood composition, function, and circulation can provide valuable insights into how hypertension affects overall health. The Dangers of High Diastolic Blood Pressure Diastolic blood pressure, the bottom number in a blood pressure reading, represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. High diastolic blood pressure can indicate underlying health issues and increase the risk of cardiovascular complications if left untreated. Heart Rate vs. Blood Pressure: Understanding the Connection Heart rate and blood pressure are closely related, with changes in one often affecting the other. Understanding the interplay between heart rate and blood pressure can help individuals monitor their cardiovascular health and make informed lifestyle choices. High Blood Pressure in Young Adults: Recognizing the Risk While high blood pressure is commonly associated with older adults, it can also affect young adults, especially those with risk factors such as obesity, poor diet, and sedentary lifestyle habits. Recognizing the signs and risk factors of hypertension in young adults is crucial for early intervention and prevention of complications. High Blood Pressure with Low Heart Rate or Pulse: What It Means In some cases, individuals may experience high blood pressure alongside a low heart rate or pulse. This combination of symptoms can indicate underlying heart or cardiovascular issues and may require further evaluation by a healthcare professional. Hypertension at 25: Addressing Early Onset High Blood Pressure While hypertension is more common in older adults, it can also occur at a young age, including in individuals as young as 25. Early detection and management of hypertension are essential for reducing the risk of long-term complications and improving overall health outcomes. The Silent Killer: Why Hypertension Goes Unnoticed Hypertension is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it typically presents with few or no noticeable symptoms until complications arise. Understanding why hypertension goes unnoticed underscores the importance of regular blood pressure screenings and proactive management strategies. What Blood Pressure is Considered Stroke Level? Certain blood pressure readings are considered indicative of a stroke risk. Understanding these thresholds can help individuals and healthcare providers identify when blood pressure levels are dangerously high and prompt prompt intervention to prevent stroke and other cardiovascular events. When is Blood Pressure Highest During the Day? Blood pressure naturally fluctuates throughout the day, with levels typically highest in the morning upon waking and gradually decreasing throughout the day. Understanding these fluctuations can help individuals monitor their blood pressure more effectively and identify potential triggers for spikes. In conclusion, hypertension is a common yet serious health condition that requires attention and proactive management. By understanding the four stages of hypertension, blood facts, and the dangers associated with high blood pressure, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of complications. Regular blood pressure monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to treatment recommendations are key components of effective hypertension management. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing your health.
Diabetes and Hypertension: A Dangerous Duo

Introduction Diabetes and hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, are two prevalent chronic conditions that often coexist in individuals. While each condition poses significant health risks on its own, their combination can exacerbate complications and lead to severe health consequences. In this article, we will explore the relationship between diabetes and hypertension in a scientific yet understandable manner for individuals without a medical background. Understanding Diabetes and Hypertension Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of insulin by the body. On the other hand, hypertension refers to high blood pressure, where the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is consistently elevated. The Interplay Between Diabetes and Hypertension Research has shown a strong correlation between diabetes and hypertension, with individuals diagnosed with diabetes being at a higher risk of developing hypertension and vice versa. This relationship is multifaceted and involves various physiological mechanisms within the body. One key factor contributing to the link between diabetes and hypertension is kidney damage. Diabetes can lead to scarring of the kidneys, impairing their ability to regulate salt and water balance in the body. As a result, excess salt and water are retained, leading to an increase in blood volume and subsequently raising blood pressure levels. Furthermore, diabetes can also damage the small blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the kidneys and the walls of the arteries. This damage causes the blood vessels to become stiff and less elastic, hindering their ability to dilate and constrict appropriately. Consequently, the resistance to blood flow increases, contributing to elevated blood pressure readings. Moreover, insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes, has been implicated in the development of hypertension. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, leading to higher insulin levels in the bloodstream. These elevated insulin levels can directly affect blood vessel function and promote the constriction of blood vessels, further contributing to hypertension. Implications and Consequences The coexistence of diabetes and hypertension significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. Individuals with both conditions require careful management and monitoring to mitigate these risks and maintain optimal health. Management Strategies Effective management of diabetes and hypertension typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, along with regular physical activity, can help control blood sugar levels and blood pressure. Additionally, medications such as antihypertensives and antidiabetic agents may be prescribed by healthcare professionals to manage both conditions effectively. Conclusion Diabetes and hypertension represent a dangerous duo, as their coexistence can lead to a cascade of adverse health outcomes. Understanding the relationship between these two conditions is crucial for individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health effectively. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and adhering to medical recommendations, individuals can reduce the impact of diabetes and hypertension on their overall well-being.
