Hypertension in Pregnancy: What You Need to Know
Hypertension during pregnancy, also known as gestational hypertension or pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH), is a condition that can pose significant risks to both the mother and the baby. Understanding the implications, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for ensuring a successful pregnancy with high blood pressure. The Relationship Between Diabetes and Hypertension During Pregnancy Diabetes and hypertension often coexist and can complicate pregnancy. Women with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing hypertension during pregnancy, which can lead to a range of complications including preeclampsia, preterm birth, and complications during delivery. Managing both conditions effectively is vital for maternal and fetal health. Normal Blood Pressure for Pregnant Women For most pregnant women, a normal blood pressure reading is below 120/80 mm Hg. However, blood pressure can vary throughout pregnancy, and slight elevations may not be immediately concerning. Regular monitoring is essential to catch any significant changes early. Low Blood Pressure During Pregnancy While high blood pressure garners most of the attention, low blood pressure during pregnancy can also be an issue. Symptoms like dizziness, fainting, and fatigue can be common. It is important to stay hydrated and avoid prolonged standing to manage these symptoms. When Should Swelling During Pregnancy Be a Concern? Swelling, particularly in the feet and ankles, is common during pregnancy. However, sudden or severe swelling, especially in the hands and face, can be a sign of preeclampsia, a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Why Do Doctors Prescribe Aspirin During Pregnancy? Doctors may prescribe low-dose aspirin during pregnancy to women who are at high risk of preeclampsia. Aspirin can help reduce the risk of developing this condition by improving placental blood flow and reducing inflammation. High Blood Pressure After Pregnancy High blood pressure can persist even after the baby is born, a condition known as postpartum hypertension. It is crucial to continue monitoring blood pressure levels and follow the doctor’s advice to manage this condition effectively. 120 Resting Heart Rate While Pregnant A resting heart rate of 120 beats per minute (bpm) can be higher than normal during pregnancy, where the typical range is 60-100 bpm. Increased heart rate can be due to the additional stress on the body as it supports the growing baby. If you notice consistently high heart rates, consult your healthcare provider. When Do You Start Showing Second Pregnancy? In the second pregnancy, women often start showing earlier than they did in their first pregnancy. This is due to the abdominal muscles being stretched from the previous pregnancy. Typically, women begin to show between 12 to 16 weeks. Managing PIH Pregnancy for a Successful Outcome Successfully managing PIH involves regular prenatal check-ups, lifestyle modifications, and possibly medication. Adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking and alcohol can help manage blood pressure levels. Key Takeaways for Managing Hypertension During Pregnancy By understanding the risks and taking proactive steps, pregnant women with hypertension can improve their chances of a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Innovations in Insulin Therapy: The Impact of Insulin Aspart

Introduction Insulin Aspart, sold under the brand name NovoLog, represents a significant advancement in insulin therapy. As a rapid-acting insulin analog, it has transformed the management of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, providing better glucose control and flexibility in meal planning. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Insulin Aspart has a quicker onset and shorter duration of action compared to regular human insulin. It begins to work within 10-20 minutes of injection, peaks at around 1-3 hours, and continues to be effective for 3-5 hours. This rapid action closely mimics the body’s natural insulin response to meals. Clinical Use NovoLog is typically administered before meals to control postprandial blood glucose levels. Its rapid action allows for more precise matching of insulin doses to carbohydrate intake, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. It is also used in insulin pumps for continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Benefits and Limitations The primary benefit of Insulin Aspart is its ability to provide better postprandial glucose control with fewer hypoglycemic episodes. However, like all insulin therapies, it requires careful monitoring and dose adjustment to achieve optimal control. Conclusion Insulin Aspart has significantly improved the management of diabetes, offering patients more flexibility and better control over their blood glucose levels. Its rapid action and efficacy make it a vital component of modern insulin therapy regimens.
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment: Advances and Innovations

Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management. At InsulinReview, we provide comprehensive reviews and insights on the latest treatments and research developments. This article explores various aspects of type 1 diabetes treatment, focusing on beta cell regeneration, stem cell therapy, and emerging treatments. Beta Cells Pancreas: The Heart of Insulin Production Beta cells pancreas are crucial for insulin production. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks these cells, leading to insulin deficiency. Understanding the role of beta cells is essential for developing effective treatments. How to Regenerate Beta Cells Naturally Research into how to regenerate beta cells naturally is ongoing, with some studies suggesting that diet, exercise, and certain natural compounds may support beta cell health. While there is no definitive method yet, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is recommended. Beta Cell Regeneration: Hope for a Cure Beta cell regeneration aims to restore the body’s ability to produce insulin. Scientists are exploring various approaches, including gene therapy, to stimulate the regeneration of these crucial cells. How to Regenerate Beta Cells in Pancreas Understanding how to regenerate beta cells in pancreas involves complex biological processes. Current research focuses on identifying factors that can trigger the growth and function of these cells, potentially reversing type 1 diabetes. How to Regenerate Pancreas Beta Cells Naturally While how to regenerate pancreas beta cells naturally remains a challenging area of research, some studies highlight the potential of natural substances, such as certain peptides and growth factors, in promoting beta cell growth. Vertex Diabetes Cure: A Promising Development The Vertex diabetes cure represents a significant breakthrough. Vertex Pharmaceuticals is developing a cell-based therapy that aims to replace damaged beta cells, offering hope for a long-term solution to type 1 diabetes. Type 1 Diabetes Beta Cells: The Focus of Research Research on type 1 diabetes beta cells is crucial for developing new treatments. Scientists are investigating how to protect and regenerate these cells to restore insulin production. Beta Cell: Central to Diabetes Treatment The beta cell is at the core of diabetes treatment. Ensuring these cells function properly is essential for managing blood glucose levels effectively. New Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes New treatment for type 1 diabetes includes advances in immunotherapy, beta cell transplantation, and gene editing technologies. These innovations aim to offer better control and potentially a cure for the condition. Pancreas Beta Cells: Essential for Insulin Production Pancreas beta cells produce insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. Protecting and regenerating these cells is key to treating type 1 diabetes. Stem Cell Diabetes: A Revolutionary Approach Stem cell diabetes research is making significant strides. Stem cells have the potential to develop into insulin-producing cells, offering a revolutionary approach to treating type 1 diabetes. Beta Cells Produce Insulin: The Biological Mechanism Beta cells produce insulin, which is crucial for glucose metabolism. Understanding this mechanism helps in developing targeted therapies for diabetes. Stem Cell Type 1 Diabetes: Cutting-Edge Research Stem cell type 1 diabetes research involves transforming stem cells into insulin-producing beta cells. This cutting-edge approach could potentially cure diabetes by restoring natural insulin production. Insulin Beta Cells: Vital for Glucose Regulation Insulin beta cells are vital for glucose regulation. Damage to these cells results in the inability to control blood sugar, highlighting the importance of beta cell health. Stem Cell Therapy Diabetes: Innovative Treatment Stem cell therapy diabetes aims to replace damaged beta cells with new, functioning ones. This innovative treatment has shown promise in early clinical trials. What Cells Make Insulin? What cells make insulin? Beta cells in the pancreas are responsible for insulin production. Protecting and regenerating these cells is a primary goal in diabetes research. Cell Therapies: A New Frontier Cell therapies for diabetes involve the transplantation of insulin-producing cells to restore normal glucose regulation. These therapies are at the forefront of diabetes treatment research. Insulin Cell: The Core of Diabetes Management The insulin cell is central to managing diabetes. Ensuring the health and functionality of these cells can significantly improve diabetes outcomes. Key Takeaways Conclusion Advances in type 1 diabetes treatment, particularly in the areas of beta cell regeneration and stem cell therapy, are paving the way for more effective management and potential cures. At InsulinReview, we remain committed to providing the latest insights and updates on these groundbreaking developments. For more detailed reviews and expert perspectives on diabetes treatments, visit InsulinReview, your trusted source for comprehensive medical information.
Long-Acting Insulin: The Benefits of Insulin Glargine
Introduction Long-Acting Insulin Insulin Glargine, known by the brand name Lantus, is a long-acting insulin analog that provides stable and prolonged glucose-lowering effects. It plays a crucial role in the basal insulin regimen for patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Mechanism of Action Long-Acting Insulin Insulin Glargine forms microprecipitates at the injection site, releasing insulin slowly and providing a steady, peakless absorption profile. This action mimics the body’s basal insulin secretion, maintaining consistent blood glucose levels over 24 hours. Clinical Use Long-Acting Insulin Lantus is typically administered once daily, providing a convenient and effective basal insulin option. It helps manage fasting blood glucose levels and reduces the risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia, a common challenge in diabetes management. Advantages Long-Acting Insulin The primary advantage of Insulin Glargine is its long, stable action, which reduces the frequency of insulin injections and helps maintain steady glucose levels. This reduces the burden of diabetes management and improves adherence to insulin therapy. Conclusion Insulin Glargine is a vital component in the management of diabetes, offering a reliable and effective solution for maintaining basal insulin levels. Its once-daily administration and stable glucose-lowering effect make it an essential tool in modern diabetes care.
Diabetes and Cognitive Function: Understanding the Connection
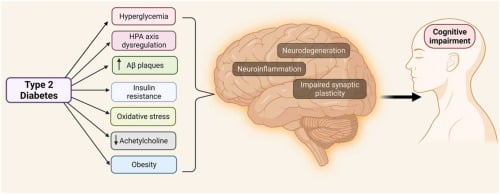
Diabetes is a chronic condition with far-reaching implications, not only for physical health but also for cognitive function. At InsulinReview, we delve into the intricate relationship between diabetes and cognitive decline, exploring how this condition affects the brain and memory. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview, backed by scientific insights and patient experiences, to understand better the cognitive challenges faced by individuals with diabetes. Diabetes and Cognitive Decline: An Overview Diabetes and cognitive decline are closely linked, with numerous studies indicating that individuals with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, are at a higher risk of developing cognitive impairment and dementia. The exact mechanisms are complex and multifactorial, involving vascular damage, chronic inflammation, and metabolic dysregulation. Type 1 Diabetes and Cognitive Decline: Specific Risks While much of the research has focused on type 2 diabetes, there is growing evidence that type 1 diabetes and cognitive decline are also connected. Individuals with type 1 diabetes may experience cognitive challenges due to prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels and episodes of severe hypoglycemia. These factors can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain over time. Diabetes and Cognitive Impairment: Key Findings Diabetes and cognitive impairment can manifest in various ways, from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to more severe forms of dementia. Key findings from research include: How Does Diabetes Affect Cognitive Function? Understanding how does diabetes affect cognitive function involves looking at several physiological and biochemical pathways: Memory and Diabetes: The Specific Impact Memory and diabetes are closely connected, with many individuals reporting memory lapses and difficulties. This can affect daily activities and quality of life, making it essential for patients and healthcare providers to monitor and address these cognitive changes. Key Takeaways Conclusion The connection between diabetes and cognitive function highlights the importance of comprehensive diabetes management that goes beyond blood sugar control. At InsulinReview, we emphasize the need for ongoing research and patient education to understand better and mitigate the cognitive challenges associated with diabetes. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with diabetes can take steps to protect their cognitive health and overall well-being. For more insights and reviews on diabetes management, visit InsulinReview, your trusted source for medical information and support.
Can You Get Rid of Diabetes?

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While managing diabetes is a lifelong commitment, many wonder if it’s possible how to reverse diabetes entirely. This article explores the potential for “can diabetes be cured,” the lifestyle changes involved, and the role of medical interventions. Understanding Diabetes: Type 1 vs. Type 2 Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells. Currently, there’s no cure for Type 1 diabetes, and management relies on insulin therapy and lifestyle adjustments. Type 2 diabetes, however, can sometimes be reversed through significant lifestyle changes. This type occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin. Factors like obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise play crucial roles. Lifestyle Changes for Managing and Reversing Type 2 Diabetes Diet Modifications A balanced diet is essential. Foods that start with K, like kale and kiwi, are nutrient-dense and beneficial for blood sugar control. Moreover, incorporating diabetic-friendly snacks, such as nuts and berries, can help manage hunger without causing blood sugar spikes. Exercise Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps in maintaining a healthy weight, which is crucial for diabetes management. Medical Interventions In some cases, medications and even surgical procedures like bariatric surgery can help manage or reverse Type 2 diabetes. Consulting with a healthcare provider is vital to determine the best approach. The Role of Superfoods and Supplements Superfoods Superfoods like berries, oatmeal, and the healthiest beans are excellent for diabetes management. These foods are high in fiber and nutrients that help control blood sugar levels. Supplements Supplements can also play a role. The best potassium supplement can aid in maintaining heart health, while the best vitamin brands and the best greens supplement can fill nutritional gaps. Conclusion While Type 1 diabetes cannot be cured, Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be reversed with significant lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and medical guidance are key components in managing this condition and possibly reversing it, and answer the question, “can diabetes disappear?”.
Understanding Trurapi Insulin: Benefits, Usage, and Comparison
Trurapi insulin is a medication commonly prescribed for individuals with diabetes to help manage blood sugar levels. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of Trurapi insulin, how it is used, and how it compares to other insulin options. What is Trurapi Insulin? Trurapi insulin, also known by its generic name insulin glargine, is a long-acting insulin analog used to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes mellitus. It provides a steady level of insulin over an extended period, helping to regulate glucose levels throughout the day. Usage and Administration Trurapi insulin is typically administered via subcutaneous injection using an insulin pen, such as the Trurapi Solostar pen. The dosage and administration instructions may vary depending on individual needs and healthcare provider recommendations. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and injection technique carefully for optimal results. Trurapi vs. Novorapid Trurapi insulin is a long-acting insulin, whereas Novorapid (insulin aspart) is a rapid-acting insulin analog. While both medications are used to manage diabetes, they have different onset and duration of action. Trurapi provides a steady release of insulin over an extended period, while Novorapid acts more quickly to lower blood sugar levels after meals. Trurapi Biosimilar Trurapi insulin may also be available as a biosimilar, which is a biological product highly similar to an existing FDA-approved reference product. Biosimilar insulins offer a more affordable alternative to brand-name insulin while maintaining comparable efficacy and safety. Conclusion Trurapi insulin is an essential medication for individuals with diabetes, providing long-acting control of blood sugar levels. With its convenient administration via insulin pen and potential availability as a biosimilar, Trurapi offers a valuable option for diabetes management. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable insulin regimen for individual needs.
Exploring Trurapi Solostar: A Convenient Insulin Delivery System
Trurapi Solostar is a popular insulin pen delivery system used by individuals with diabetes to administer Trurapi insulin. In this article, we’ll delve into the features of Trurapi Solostar, its usage, and how it enhances insulin administration for diabetes management. What is Trurapi Solostar? Trurapi Solostar is a pre-filled insulin pen designed for the administration of Trurapi insulin (insulin glargine). It offers a convenient and user-friendly way for individuals with diabetes to administer their insulin doses accurately. Key Features Usage and Administration To use Trurapi Solostar, users simply dial their prescribed insulin dosage, insert a new needle, prime the pen if necessary, and administer the injection subcutaneously. The pen’s clear dose window and audible click provide visual and tactile feedback to ensure accurate dosing. Advantages of Trurapi Solostar Conclusion Trurapi Solostar is a valuable insulin delivery system for individuals with diabetes, offering convenience, accuracy, and portability in insulin administration. Its user-friendly design makes it a preferred choice for many individuals managing diabetes, providing peace of mind and effective blood sugar control. If you are considering Trurapi Solostar for your insulin therapy, consult with your healthcare provider to determine if it is the right option for you.
