Why Am I Not Losing Weight on Victoza?

There could be several reasons why you might not be losing weight on Victoza, a medication primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes but also prescribed for weight loss. It’s important to ensure that the dosage is optimized for your specific needs and that you’re following your doctor’s recommendations. Additionally, Victoza is most effective when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise. Individual responses to the medication can vary, so while some may see significant weight loss, others might not. Other medical conditions, hormonal imbalances, or medications could also interfere with your weight loss efforts, and it’s important to remember that weight loss can be gradual, taking several weeks or months to notice significant changes. Victoza Weight Loss Reviews Reviews on Victoza for weight loss are mixed. Some users report substantial weight loss and improved appetite control, while others experience minimal results. It’s crucial to consider these varied experiences and consult with your healthcare provider to determine if Victoza is right for you. Victoza Weight Loss Mechanism Victoza works by mimicking the GLP-1 hormone, which regulates appetite and insulin. This helps control blood sugar levels and reduce appetite, leading to potential weight loss. However, individual results can vary based on several factors, including adherence to lifestyle changes like diet and exercise. Victoza Side Effects Common side effects of Victoza include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, headache, and dizziness. More severe side effects can include pancreatitis, gallbladder disease, kidney problems, and allergic reactions. It’s important to monitor for these side effects and consult your healthcare provider if they occur. Victoza Pen The Victoza pen is a pre-filled, multi-dose injectable device designed for easy use. It allows for dosage adjustment via a dial, making it convenient for daily administration. Using Victoza for Weight Loss Although Victoza is sometimes prescribed off-label for weight loss, particularly in patients with obesity or those who are overweight with related health conditions, it’s important to follow medical advice for its use. Foods to Avoid on Victoza While taking Victoza, it’s advisable to avoid high-fat and high-sugar foods to maximize weight loss benefits. Eating a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains, and limiting alcohol intake can help improve results. Dosing for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics For weight loss in non-diabetics, the dosing typically starts at 0.6 mg per day and can be gradually increased to 1.2 mg or 1.8 mg per day, depending on the patient’s response and tolerance. Always follow your healthcare provider’s dosing instructions. Victoza Coupons and Cost Coupons for Victoza can often be found through the manufacturer’s website or various prescription savings programs, which can help reduce the out-of-pocket cost. Without insurance, the cost of Victoza can range from $800 to $1,000 per month, but with insurance or a savings program, this cost may be significantly reduced. Best Time to Take Victoza for Weight Loss Victoza is typically taken once daily, at any time, with or without food. However, taking it at the same time each day can help establish a routine and ensure consistent adherence to the medication. If you have further questions or need more detailed information, feel free to ask!
Does Mounjaro Cause Hair Loss? The Truth Revealed!

As diabetes treatments evolve, new medications such as Mounjaro (tirzepatide) have shown promise. However, with these advancements come concerns about side effects, including hair loss. This article will explore whether Mounjaro causes hair loss, and compare it to other diabetes medications that may have similar side effects. Understanding Mounjaro and Hair Loss Does Mounjaro Cause Hair Loss? Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is a newer diabetes medication that has generated significant interest due to its effectiveness. However, some users have reported experiencing hair loss while on this medication. This has led to the question: does Mounjaro cause hair loss? Mounjaro Side Effects Hair Loss While hair loss is not listed as a common side effect of Mounjaro, anecdotal reports from patients suggest a possible connection. Hair loss with Mounjaro might be due to the body’s response to a new medication or other underlying factors such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, or hormonal changes. Comparisons with Other Diabetes Medications Does Farxiga Cause Hair Loss? Farxiga (dapagliflozin) is another diabetes medication that some users have linked to hair loss. While not a widespread issue, it highlights that different medications can affect individuals uniquely. Rybelsus Side Effects Hair Loss Rybelsus (semaglutide) has also been associated with hair loss in some patients. Like with Mounjaro, this side effect is not officially documented but reported anecdotally. Does Trulicity Cause Hair Loss? Trulicity (dulaglutide) users have also reported hair loss, though it is not a common or well-documented side effect. Each patient’s response to medication can vary significantly. How to Stop Hair Loss from Mounjaro If you are experiencing hair loss from Mounjaro, consider the following steps: Other Related Medications and Hair Loss Can Phentermine Cause Hair Loss? Phentermine, a weight loss medication, has been reported to cause hair loss in some users. This underscores the importance of monitoring side effects when taking any medication. Tirzepatide and Hair Loss Since tirzepatide is the active ingredient in Mounjaro, understanding its side effects is crucial. Though not widely reported, tirzepatide hair loss could still be a concern for some users. Does Saxenda Cause Hair Loss? Saxenda (liraglutide) is another medication where hair loss has been noted as a potential side effect by some users, although it is not common. Addressing Hair Loss: Practical Tips How to Stop Mounjaro Hair Loss Overnight While stopping hair loss overnight may not be feasible, taking steps such as maintaining a healthy diet, using gentle hair care products, and avoiding excessive styling can help mitigate the issue. Mounjaro Hair Loss Reviews Female Reviews from female users of Mounjaro often highlight concerns about hair loss. It’s essential to gather comprehensive information and consult with healthcare providers to address these concerns effectively. Conclusion Hair loss from Mounjaro is not officially recognized as a common side effect, but patient reports indicate it may occur in some individuals. If you experience this issue, consult your healthcare provider for guidance and consider potential alternatives or supportive treatments. Key Takeaways For more in-depth reviews and professional insights on diabetes medications, visit InsulinReview.
The Role of Metformin in Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Introduction Metformin, marketed under the brand name Glucophage, is a cornerstone in the management of type 2 diabetes. This oral antidiabetic medication has been extensively studied and remains a first-line therapy due to its efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness. Mechanism of Action Metformin works primarily by decreasing hepatic glucose production and improving insulin sensitivity, which enhances peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. Unlike other antidiabetic drugs, metformin does not cause significant hypoglycemia when used as monotherapy, making it a safer option for many patients. Clinical Applications Metformin is recommended as the initial pharmacologic treatment for type 2 diabetes in conjunction with lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise. It is particularly effective in overweight or obese patients due to its favorable effects on weight loss and cardiovascular risk factors. Adverse Effects The most common side effects of metformin are gastrointestinal, including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal discomfort. These effects can often be mitigated by starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it. Rarely, metformin can cause lactic acidosis, a serious but uncommon condition. Conclusion Metformin continues to be a foundational treatment for type 2 diabetes, offering significant benefits in glucose control, weight management, and cardiovascular health. Its long-standing use and extensive research support its role as a first-line therapy in managing this chronic condition.
Innovations in Insulin Therapy: The Impact of Insulin Aspart

Introduction Insulin Aspart, sold under the brand name NovoLog, represents a significant advancement in insulin therapy. As a rapid-acting insulin analog, it has transformed the management of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, providing better glucose control and flexibility in meal planning. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics Insulin Aspart has a quicker onset and shorter duration of action compared to regular human insulin. It begins to work within 10-20 minutes of injection, peaks at around 1-3 hours, and continues to be effective for 3-5 hours. This rapid action closely mimics the body’s natural insulin response to meals. Clinical Use NovoLog is typically administered before meals to control postprandial blood glucose levels. Its rapid action allows for more precise matching of insulin doses to carbohydrate intake, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia. It is also used in insulin pumps for continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Benefits and Limitations The primary benefit of Insulin Aspart is its ability to provide better postprandial glucose control with fewer hypoglycemic episodes. However, like all insulin therapies, it requires careful monitoring and dose adjustment to achieve optimal control. Conclusion Insulin Aspart has significantly improved the management of diabetes, offering patients more flexibility and better control over their blood glucose levels. Its rapid action and efficacy make it a vital component of modern insulin therapy regimens.
Long-Acting Insulin: The Benefits of Insulin Glargine
Introduction Long-Acting Insulin Insulin Glargine, known by the brand name Lantus, is a long-acting insulin analog that provides stable and prolonged glucose-lowering effects. It plays a crucial role in the basal insulin regimen for patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Mechanism of Action Long-Acting Insulin Insulin Glargine forms microprecipitates at the injection site, releasing insulin slowly and providing a steady, peakless absorption profile. This action mimics the body’s basal insulin secretion, maintaining consistent blood glucose levels over 24 hours. Clinical Use Long-Acting Insulin Lantus is typically administered once daily, providing a convenient and effective basal insulin option. It helps manage fasting blood glucose levels and reduces the risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia, a common challenge in diabetes management. Advantages Long-Acting Insulin The primary advantage of Insulin Glargine is its long, stable action, which reduces the frequency of insulin injections and helps maintain steady glucose levels. This reduces the burden of diabetes management and improves adherence to insulin therapy. Conclusion Insulin Glargine is a vital component in the management of diabetes, offering a reliable and effective solution for maintaining basal insulin levels. Its once-daily administration and stable glucose-lowering effect make it an essential tool in modern diabetes care.
Oral Agents in Diabetes: The Efficacy of Glimepiride
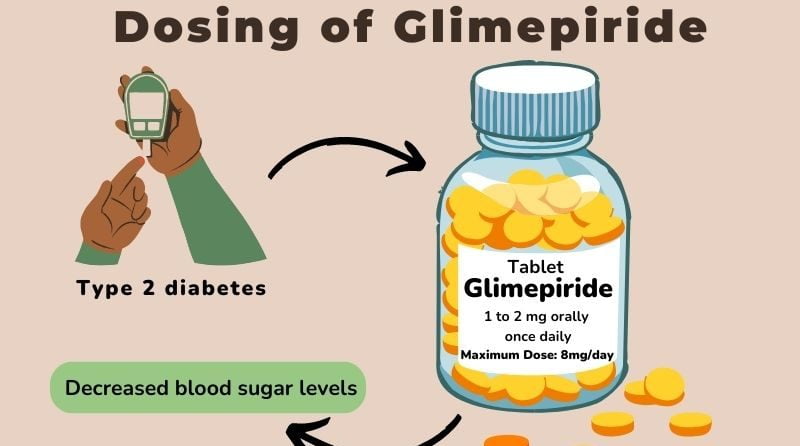
Introduction Glimepiride Glimepiride, marketed under the brand name Amaryl, is a sulfonylurea class antidiabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It stimulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, thereby helping to lower blood glucose levels. Mechanism of Action Glimepiride Glimepiride works by binding to sulfonylurea receptors on pancreatic beta cells, leading to increased insulin release. This enhances glucose uptake by tissues and reduces hepatic glucose production, contributing to lower blood glucose levels. Clinical Applications Glimepiride Glimepiride is often used when lifestyle modifications and metformin are insufficient to control blood glucose. It can be used as monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic agents, including insulin, to achieve better glycemic control. Glimepiride Side Effects and Considerations Common side effects of Glimepiride include hypoglycemia, weight gain, and gastrointestinal disturbances. Hypoglycemia is a significant risk, particularly in elderly patients or those with renal impairment, necessitating careful dose adjustment and monitoring. Conclusion Glimepiride is an effective oral antidiabetic agent that provides substantial benefits in managing type 2 diabetes. However, its use requires careful monitoring to mitigate the risk of hypoglycemia and other adverse effects.
Diabetes and Cognitive Function: Understanding the Connection
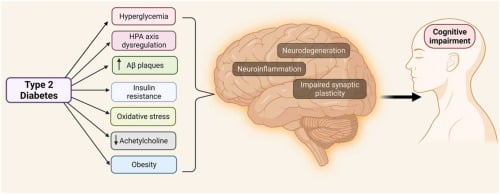
Diabetes is a chronic condition with far-reaching implications, not only for physical health but also for cognitive function. At InsulinReview, we delve into the intricate relationship between diabetes and cognitive decline, exploring how this condition affects the brain and memory. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview, backed by scientific insights and patient experiences, to understand better the cognitive challenges faced by individuals with diabetes. Diabetes and Cognitive Decline: An Overview Diabetes and cognitive decline are closely linked, with numerous studies indicating that individuals with diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, are at a higher risk of developing cognitive impairment and dementia. The exact mechanisms are complex and multifactorial, involving vascular damage, chronic inflammation, and metabolic dysregulation. Type 1 Diabetes and Cognitive Decline: Specific Risks While much of the research has focused on type 2 diabetes, there is growing evidence that type 1 diabetes and cognitive decline are also connected. Individuals with type 1 diabetes may experience cognitive challenges due to prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels and episodes of severe hypoglycemia. These factors can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain over time. Diabetes and Cognitive Impairment: Key Findings Diabetes and cognitive impairment can manifest in various ways, from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to more severe forms of dementia. Key findings from research include: How Does Diabetes Affect Cognitive Function? Understanding how does diabetes affect cognitive function involves looking at several physiological and biochemical pathways: Memory and Diabetes: The Specific Impact Memory and diabetes are closely connected, with many individuals reporting memory lapses and difficulties. This can affect daily activities and quality of life, making it essential for patients and healthcare providers to monitor and address these cognitive changes. Key Takeaways Conclusion The connection between diabetes and cognitive function highlights the importance of comprehensive diabetes management that goes beyond blood sugar control. At InsulinReview, we emphasize the need for ongoing research and patient education to understand better and mitigate the cognitive challenges associated with diabetes. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with diabetes can take steps to protect their cognitive health and overall well-being. For more insights and reviews on diabetes management, visit InsulinReview, your trusted source for medical information and support.
Managing Diabetes with Glyburide: An Overview

Introduction Glyburide Glyburide, sold under the brand name Diabeta, is another sulfonylurea used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It functions similarly to glimepiride by stimulating insulin release from pancreatic beta cells. Mechanism of Action Glyburide Glyburide increases insulin secretion by binding to specific receptors on pancreatic beta cells. This leads to enhanced glucose uptake by tissues and decreased hepatic glucose production, helping to lower blood glucose levels. Clinical Use Glyburide Glyburide is used as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. It can be combined with other antidiabetic medications, including metformin and insulin, for improved efficacy. Adverse Effects Glyburide The most common side effects of Glyburide include hypoglycemia and weight gain. Hypoglycemia is a major concern and requires patients to be vigilant about monitoring their blood glucose levels, particularly when their physical activity or dietary intake changes. Conclusion Glyburide remains a valuable option in the armamentarium of type 2 diabetes treatments. Its ability to effectively lower blood glucose levels makes it an important tool, although it must be used with caution to prevent hypoglycemia.
Sitagliptin: A DPP-4 Inhibitor for Diabetes Management

Introduction Sitagliptin Sitagliptin, marketed under the brand name Januvia, is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor used to treat type 2 diabetes. It enhances the body’s natural ability to regulate blood sugar by increasing the levels of incretin hormones. Mechanism of Action Sitagliptin Sitagliptin works by inhibiting the enzyme DPP-4, which breaks down incretin hormones. These hormones increase insulin release from pancreatic beta cells and decrease glucagon secretion from alpha cells, resulting in lower blood glucose levels. Clinical Applications Sitagliptin (Januvia) Januvia is often prescribed in combination with other antidiabetic medications, such as metformin, to improve glycemic control. It is well-tolerated and associated with a low risk of hypoglycemia, making it a suitable option for many patients. Side Effects Sitagliptin (Januvia) Common side effects of Sitagliptin include upper respiratory tract infections, headaches, and nasopharyngitis. It has a favorable safety profile, but rare cases of pancreatitis have been reported, necessitating careful monitoring. Conclusion Sitagliptin is a valuable addition to the diabetes treatment landscape, offering an effective and well-tolerated option for improving glycemic control. Its mechanism of action and low risk of hypoglycemia make it a preferred choice for many patients.
Can You Get Rid of Diabetes?

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While managing diabetes is a lifelong commitment, many wonder if it’s possible how to reverse diabetes entirely. This article explores the potential for “can diabetes be cured,” the lifestyle changes involved, and the role of medical interventions. Understanding Diabetes: Type 1 vs. Type 2 Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells. Currently, there’s no cure for Type 1 diabetes, and management relies on insulin therapy and lifestyle adjustments. Type 2 diabetes, however, can sometimes be reversed through significant lifestyle changes. This type occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin. Factors like obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise play crucial roles. Lifestyle Changes for Managing and Reversing Type 2 Diabetes Diet Modifications A balanced diet is essential. Foods that start with K, like kale and kiwi, are nutrient-dense and beneficial for blood sugar control. Moreover, incorporating diabetic-friendly snacks, such as nuts and berries, can help manage hunger without causing blood sugar spikes. Exercise Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps in maintaining a healthy weight, which is crucial for diabetes management. Medical Interventions In some cases, medications and even surgical procedures like bariatric surgery can help manage or reverse Type 2 diabetes. Consulting with a healthcare provider is vital to determine the best approach. The Role of Superfoods and Supplements Superfoods Superfoods like berries, oatmeal, and the healthiest beans are excellent for diabetes management. These foods are high in fiber and nutrients that help control blood sugar levels. Supplements Supplements can also play a role. The best potassium supplement can aid in maintaining heart health, while the best vitamin brands and the best greens supplement can fill nutritional gaps. Conclusion While Type 1 diabetes cannot be cured, Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be reversed with significant lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and medical guidance are key components in managing this condition and possibly reversing it, and answer the question, “can diabetes disappear?”.
